The quick version
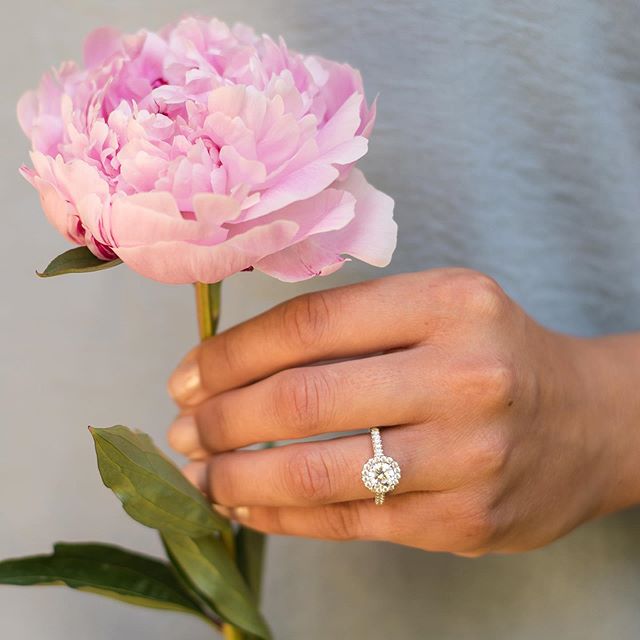
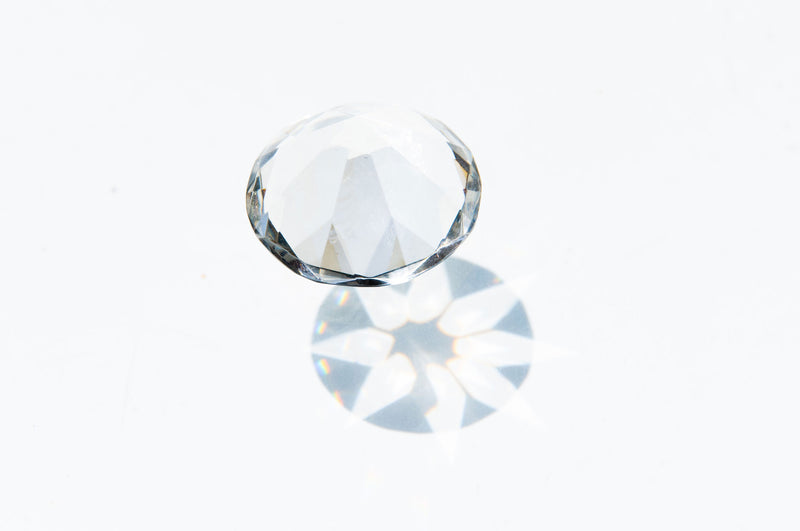
In short, lab grown diamonds are created in a lab instead of being dug out the earth
They're 100% real diamonds. Visually and chemically identical to their mined counterparts.
They're much more environmentally friendly with none poor working conditions found in most diamond mines. And they're one of the only types of diamond which can be guaranteed as conflict-free.
And they'll save you money too.
What's not to love?